Three Articles Of The Treaty Of Waitangi
The treaty Waitangi has three articles which outline the duty and obligation of the crown and the other treaty partner which are Maori people. Treaty of Waitangi has three articles which are described as follows.

Te Tiriti O Waitangi Treaty Of Waitangi The British Library
Māori retaining their sovereignty over their valued posessions.

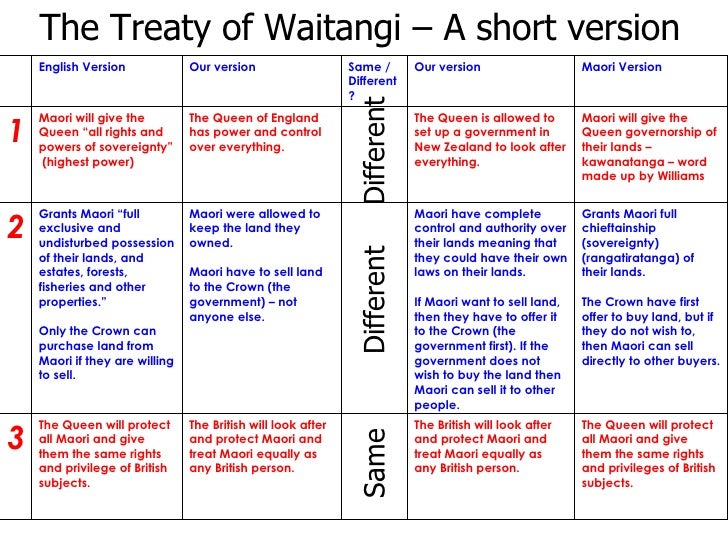
Three articles of the treaty of waitangi. It agrees to partnership with Maori to protect their own interests. Māori give the Crown an exclusive right to buy lands they wish to sell and in return are guaranteed full. The meaning of the treaty in Māori differed from the meaning in English.
Article 2 Tino Rangatiratanga. Unfortunately in the early 1860s conflict erupted in Taranaki and the Waikato in what became known as the New. The Treaty of Waitangi which is NOT Te Tiriti o Waitangi could never expect to get a microsecond of credibility it did not deserve Alan.
Chiefs gave the queen all the rights and powers of sovereignty over the land. The 2019 Hauora report recommends the following principles for the primary health care system 4. Rangatiratanga chieftainship not mana leadership which was stated in the Declaration of Independence just five years before the treaty was signed which is retained by the chiefs in.
The Queen will protect all the Māori people of New Zealand and give them all the same rights as those of the people of England. It includes being responsive to the needs of Maori and this document ensures. Essentially the endorsed the three article of the Treaty of Waitangi.
Are there 4 articles in the Treaty of Waitangi. Article 3 is about Tāngata Whenua Māori and Tāngata Tiriti all those that came to be in NZ as partners to the. A recent translation of the articles of the Māori version follows.
The principles of Te Tiriti o Waitangi as articulated by the Courts and the Waitangi Tribunal provide the framework for how we will meet our obligations under Te Tiriti in our day-to-day work. The First The chiefs of the Confederation and all the chiefs who have not joined that Confederation give absolutely to the Queen of England for ever the complete government over their land. The right to govern was given to the Crown by Māori.
There were plans made for the government to set up tribes with wide powers of local government equivalent to states in the USA runanga and to have annual conferences of chiefs. Te Tiriti the only bona fide Treaty at stake here didnt and doesnt and never will need to be reinterpreted in the most favourable possible way to Maori because it was written that way to. What are the 3 articles of the Treaty of Waitangi.
New Zealand has also signed the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights an international law to protect the rights of minorities. The Treaty of Waitangi principle isnt just about studying Treaty history or having a kapa haka group. This right is also protected under the New Zealand Bill of Rights Act and the Human Rights Act.
Thats the short of it. The Waitangi Tribunal has found the Crown actively breaching the Treaty of Waitangi on multiple levels in its vaccination strategy and shift to the traffic light system. Waikato Regional Council 2019.
The Treaty is a broad statement of principles on which the British and Māori made a political compact to found a nation state and build a government in New Zealand. Treaty of Waitangi principles. The document has three articles.
Te Tiriti versus The Treaty The document itself has three articles covering sovereignty land and rights. According to this article Maori gave the right of conduct to Britishers and in the back they want protection and authority to manage their own events but in the English version it says Maori give up sovereignty. In the English version Māori cede the sovereignty of New Zealand to Britain.
For 163 years the treaty has had three articles. The most critical difference between the texts revolves around the interpretation of three Māori words. Treaty of Waitangi 3 Article 3 This is the arrangement for the consent to the governorship of the Queen.
Article One the government gained the right to govern kawanatanga Article Two the Crown promised that Māori will have the right to make decisions over resources and taonga which they wish to retain rangatiratanga Article Three the Crown promised that its obligations to New Zealand citizens are owed equally to Māori. Article 1 is about Kāwanatanga. Kāwanatanga governorship which is ceded to the Queen in the first article.
It is about making our countrys bicultural foundations evident in school policies organisation physical spaces whānau and community. Thats the short of it. There are three articles to te Tiriti o Waitangi in a nutshell.
For example Article III of the Treaty of Waitangi sets out the right to equality before the law. The Queen will protect all the Māori people of New Zealand and give them all the same rights as those of the people of England. It is designed to establish new rights and obligation.
Treaty of Waitangi 3 Article 3. In this document Maori have certain rights. The Treaty of Waitangi principle calls for schools to understand and honour Treaty principles in all actions and decision making.
Chiefs gave the queen te Kawanatanga katoa the governance or government over the land. Article 2 is about Tino rangatiratanga. This is the arrangement for the consent to the governorship of the Queen.
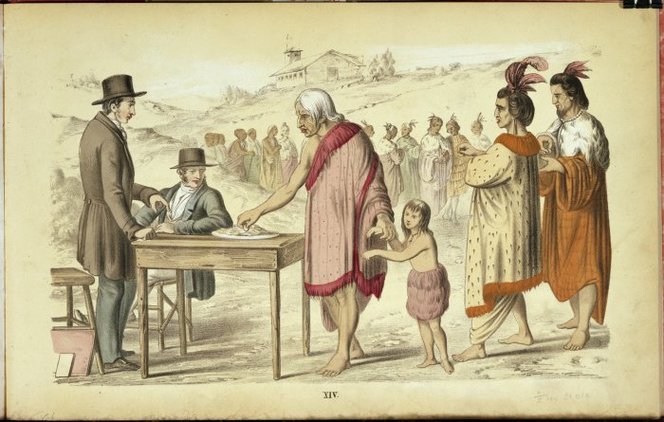

Interpretations And Meaning Of The Treaty Of Waitangi Christchurch City Libraries

Museum Of New Zealand Te Papa Tongarewa Fotoeins Fotografie

The Three Articles Of The Treaty Of Waitangi Nation And Government Te Ara Encyclopedia Of New Zealand

Treaty Of Waitangi Principle Principles Kia Ora Nz Curriculum Online
Resource 10 Drafting The Treaty
Posting Komentar untuk "Three Articles Of The Treaty Of Waitangi"